What Causes a Neck Lump?
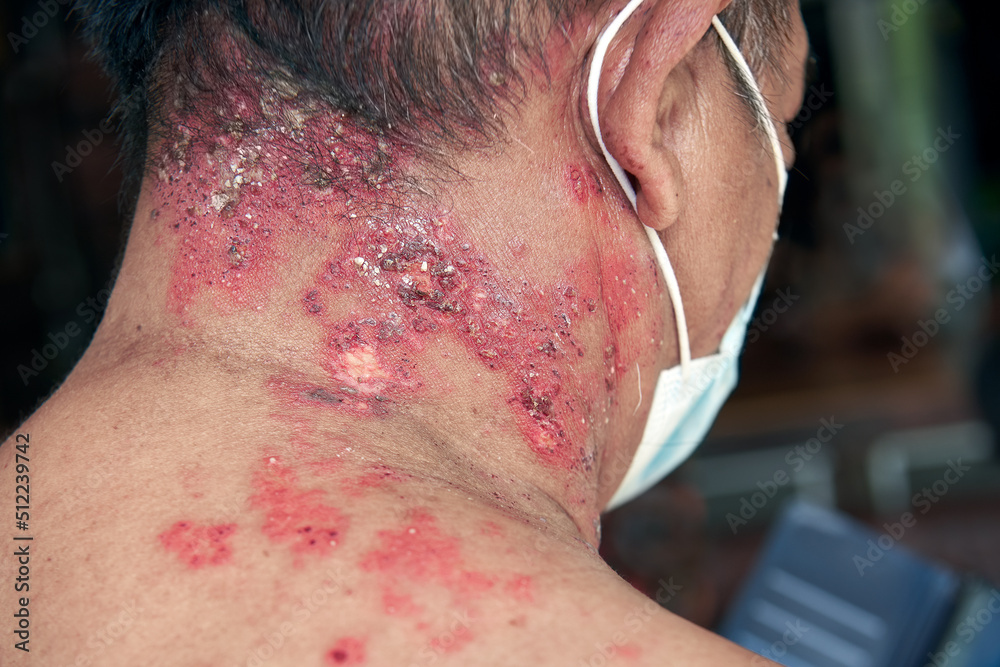
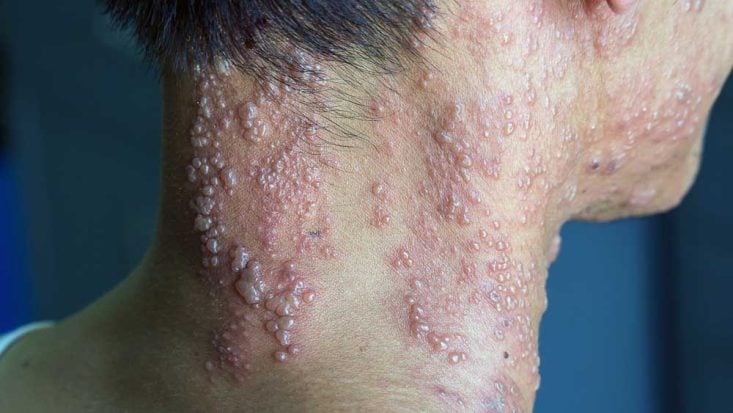
A lump on your neck can result from a viral infection or a benign growth. But sometimes it may indicate an underlying condition.
A lump on the neck is also called a neck mass. Neck lumps or masses can be large and visible, or they can be very small. Most neck lumps aren’t harmful. Most are also benign, or noncancerous. But a neck lump can also be a sign of a serious condition, such as an infection or a cancerous growth.
If you have a neck lump, your healthcare provider should evaluate it promptly. See your healthcare provider right away if you have an unexplained neck mass.
An enlarged lymph node is the most common cause of a neck lump. Lymph nodes contain cells that help your body fight off infections and attack malignant cells, or cancer. When you’re sick, your lymph nodes can become enlarged to help fight the infection. Other common causes of enlarged lymph nodes include:
- ear infections
- sinus infections
- tonsillitis
- strep throat
- dental infections
- bacterial infections of the scalp
There are other illnesses that can cause a neck lump:
- Autoimmune diseases, cancer, and other disorders of the thyroid gland, such as goiter due to iodine deficiency, can cause enlargement of part or all of your thyroid gland.
- Viruses, such as mumps, can make your salivary glands enlarged.
- Injury or torticollis can cause a lump in your neck muscles.
- Other benign neck masses include branchial clefts, thyroglossal duct cysts, dermoids, salivary masses, or ranulas.
Cancer
Most neck lumps are benign, but cancer is a possible cause. For adults, the chance that a neck lump is cancerous increases after the age of 50. Lifestyle choices, such as smoking and drinking, can also have an impact.
Prolonged use of tobacco and alcohol are the two greatest risk factorsTrusted Source for cancers of the mouth and throat, according to the American Cancer Society (ACS).
Another common risk factor for cancers of the neck, throat, and mouth is a human papillomavirus (HPV) infection. This infection is generally transmitted sexually, and it’s very common. The ACS states that signs of an HPV infection are now found in two-thirds of all throat cancers.
Cancers that show up as a lump in the neck could include:
- thyroid cancer
- cancers of the head and neck tissues
- Hodgkin’s lymphoma
- non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma
- leukemia
- other types of cancer, including lung, throat, and breast cancer
- forms of skin cancer, such as basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma
Viruses
When we think of viruses, we commonly think of the common cold and the flu. However, there are plenty of other viruses that can infect humans, many of which can cause a lump in the neck. These include:
- HIV
- herpes simplex
- infectious mononucleosis, or mono
- rubella
- tonsillitis
- viral pharyngitis
Bacteria
A bacterial infection can cause neck and throat problems, leading to inflammation and a neck lump. They include:
- infection from atypical mycobacterium, a type of bacteria most common in people with compromised immune systems and lung disease
- cat scratch fever
- strep throat
- tuberculosis
- bacterial pharyngitis
Many of these infections may be treated with prescription antibiotics.
Other possible causes
Neck lumps might also be caused by lipomas, which develop under the skin. They may also be caused by a branchial cleft cyst or thyroid nodules.
There are other, less common causes of neck lumps. Allergic reactions to medication and food can cause neck lumps. A stone in the salivary duct, which can block saliva, can also cause a neck lump.
Many conditions can cause neck lumps. Here is a list of 19 possible causes.
Warning: graphic images ahead.
Swollen lymph nodes

- Lymph nodes become swollen in response to illness, infection, medications, and stress, or, more rarely, cancer and autoimmune disease
- Swollen nodes may be tender or painless, and located in one or more places throughout the body
- Small, firm, bean-shaped lumps appear in the armpits, under the jaw, on the sides of the neck, in the groin, or above the collarbone
- Lymph nodes are considered swollen when they are larger than 1 to 2 cm in size
Goiter

- A goiter is an abnormal growth of the thyroid gland
- It may be benign or associated with increases or decreases in thyroid hormone
- Goiters may be nodular or diffuse
- Enlargement may cause difficulty swallowing or breathing, coughing, hoarseness, or dizziness when you raise your arm above your head
Tonsillitis

- This is a viral or bacterial infection of the tonsil lymph nodes
- Symptoms include sore throat, difficulty swallowing, fever, chills, headache, bad breath
- Swollen, tender tonsils and white or yellow spots on tonsils may also occur
Hodgkin’s disease

- The most common symptom is painless swelling of the lymph nodes
- Hodgkins disease may cause night sweats, itchy skin, or unexplained fever
- Fatigue, unintended weight loss, or persistent cough are other symptoms
Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma

- Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma is a diverse group of white blood cell cancers
- Classic B symptoms include fever, night sweats, and unintentional weight loss
- Other possible symptoms include painless, swollen lymph nodes, enlarged liver, enlarged spleen, skin rash, itching, fatigue, and abdominal swelling
Thyroid cancer
- This cancer occurs when normal cells in the thyroid become abnormal and start to grow out of control
- It’s the most common form of endocrine cancer with multiple subtypes
- Symptoms include lump in the throat, cough, hoarse voice, pain in the throat or neck, difficulty swallowing, swollen lymph nodes in neck, swollen or lumpy thyroid gland
Lipoma
- Soft to the touch and moves easily if prodded with your finger
- Small, just under the skin, and pale or colorless
- Commonly located in the neck, back, or shoulders
- Only painful if it grows into nerves
Mumps

- Mumps is an extremely contagious disease caused by the mumps virus It spreads by saliva, nasal secretions, and close personal contact with infected people
- Fever, fatigue, body aches, headache and loss of appetite are common
- Inflammation of the salivary (parotid) glands causes swelling, pressure, and pain in the cheeks
- Complications of infection include inflammation of the testicles (orchitis), inflammation of the ovaries, meningitis, encephalitis, pancreatitis, and permanent hearing loss
- Vaccination protects against mumps infection and mumps complications
Bacterial pharyngitis

- Bacterial pharyngitis is inflammation in the back of the throat caused by a bacterial or viral infection
- It causes a sore, dry, or scratchy throat accompanied by other symptoms such as fever, chills, body aches, nasal congestion, swollen lymph nodes, headache, cough, fatigue, or nausea
- The duration of symptoms depends on the cause of the infection
Throat cancer

- This encompasses cancer of the voice box, the vocal cords, and other parts of the throat, such as the tonsils and oropharynx
- It may occur in the form of squamous cell carcinoma or adenocarcinoma
- Symptoms include voice changes, difficulty swallowing, weight loss, sore throat, cough, swollen lymph nodes, and wheezing
- It’s most common in people with a history of smoking, excessive alcohol use, vitamin A deficiency, exposure to asbestos, oral HPV, and poor dental hygiene
Actinic keratosis
- Typically less than 2 cm, or about the size of a pencil eraser
- Thick, scaly, or crusty skin patch
- Appears on parts of the body that receive a lot of sun exposure (hands, arms, face, scalp, and neck)
- Usually pink in color but can have a brown, tan, or gray base
Basal cell carcinoma
- Raised, firm, and pale areas that may resemble a scar
- Dome-like, pink or red, shiny, and pearly areas that may have a sunk-in center, like a crater
- Visible blood vessels on the growth
- Easy bleeding or oozing wound that doesn’t seem to heal, or heals and then reappears
Squamous cell carcinoma
- Often occurs in areas exposed to UV radiation, such as the face, ears, and back of the hands
- Scaly, reddish patch of skin progresses to a raised bump that continues to grow
- Growth that bleeds easily and doesn’t heal, or heals and then reappears
Melanoma
- The most serious form of skin cancer, more common in fair-skinned people
- Mole anywhere on the body that has irregularly shaped edges, asymmetrical shape, and multiple colors
- Mole that has changed color or gotten bigger over time
- Usually larger than a pencil eraser
Rubella

- This viral infection is also known as German measles
- A pink or red rash begins on the face and then spreads downward to the rest of the body
- Mild fever, swollen and tender lymph nodes, runny or stuffy nose, headache, muscle pain, inflamed or red eyes are some symptoms
- Rubella is a serious condition in pregnant women, as it may cause congenital rubella syndrome in the fetus
- It’s prevented by receiving normal childhood vaccinations
Cat-scratch fever
- This disease is contracted from the bites and scratches of cats infected with Bartonella henselae bacteria
- A bump or blister appears at the bite or scratch site
- Swollen lymph nodes near the bite or scratch site Low fever, fatigue, headache, body aches are some of its symptoms









